Parler
Parler Gab
Gab
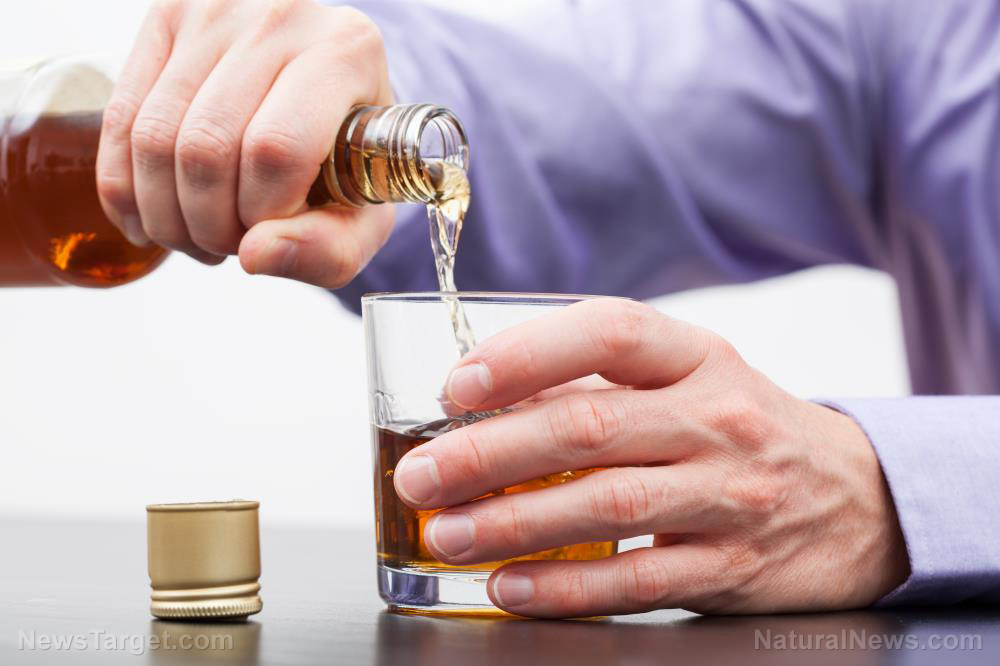
- Caffeine disrupts deep sleep by locking the brain into an overly active state, reducing restorative rest and memory consolidation.
- A new study found caffeine increases wakefulness-linked beta waves while suppressing deep-sleep delta waves, leaving the brain unable to recover properly.
- Young adults (ages 20 to 27) suffer more due to higher adenosine receptors, making their sleep more chaotic and less restorative than older adults.
- Experts recommend cutting off caffeine by early afternoon to avoid sleep interference, especially for those under 40.
- Chronic caffeine-induced sleep deprivation harms immunity, memory, and stress levels, emphasizing the need for better sleep hygiene over stimulant reliance.
The brain’s "criticality" crisis
Caffeine pushes the brain into a state of "criticality," a term scientists use to describe a hyper-alert balance between order and chaos. "It’s like an orchestra: too quiet and nothing happens, too chaotic and there’s cacophony," said study co-author Karim Jerbi, a psychology professor at Mila-Quebec AI Institute. While this state enhances focus during waking hours, it becomes destructive at night. The study found caffeine increased beta waves (linked to wakefulness) while suppressing delta waves, which are crucial for deep sleep. "The brain would neither relax nor recover properly," warned Julie Carrier, a sleep and psychology professor involved in the research. Even when participants fell asleep, their brain signals were more erratic, resembling an awake mind rather than one at rest.Younger brains suffer more
The impact was worse for adults under 30. Younger participants showed heightened neural complexity during REM sleep, the phase tied to dreaming and emotional processing. The reason? Adenosine receptors, which caffeine blocks to prevent drowsiness, are more abundant in young brains. As people age, these receptors decline, making caffeine less disruptive for middle-aged adults. This explains why a 25-year-old might toss and turn after a late-day latte, while a 50-year-old feels fewer repercussions. But the consequences extend beyond fatigue: impaired sleep quality sabotages memory retention, learning, and cellular repair.How to enjoy caffeine without wrecking sleep
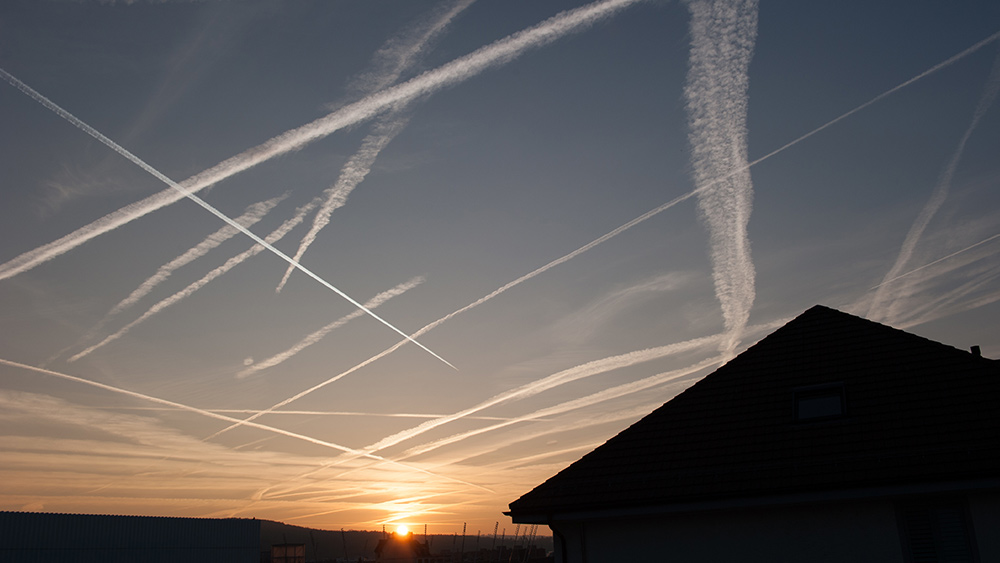
Health-conscious consumers don’t need to abandon coffee entirely, but timing is everything. Experts recommend cutting off caffeine by early afternoon to avoid interference with sleep cycles. "You want caffeine to work for you, not against you," advised Dr. Joseph Mercola, a family physician. For those under 40, he suggests a "caffeine reset" if sleep trackers show fragmented rest. Alternatives like decaf herbal teas or adaptogenic drinks can provide energy without the neural chaos. And for those who rely on caffeine for productivity, shifting consumption to morning hours ensures the brain has time to metabolize stimulants before bedtime. Chronic sleep deprivation fueled by caffeine has cascading health effects, from weakened immunity to accelerated aging. Deep sleep is when the brain processes and stores information; without it, cognitive function declines and stress hormones spike. The study’s machine-learning analysis could distinguish caffeinated sleep from normal rest with 75% accuracy, which is proof of caffeine’s profound neural disruption. While the FDA considers moderate caffeine safe, this research underscores the need for personalized limits, especially for young adults. Caffeine’s grip on modern culture is undeniable, but its stealthy sabotage of sleep demands scrutiny. As this study reveals, the stimulant doesn’t just keep you awake; it rewires your brain’s nighttime activity, leaving you exhausted even after hours in bed. For those seeking true vitality, the solution isn’t more caffeine but better sleep hygiene. By respecting the brain’s need for uninterrupted recovery, we can harness caffeine’s benefits without sacrificing long-term health. Sources for this article include: TheEpochTimes.com SciTechDaily.com StudyFinds.org ScienceAlert.comAluminum in the skies: Neurosurgeon exposes link to brain crisis
By Willow Tohi // Share
Health Ranger Report: Xlear’s Nathan Jones recounts his fight against government overreach
By Kevin Hughes // Share
FDA halts clinical trials shipping American cells overseas due to national security risks
By Willow Tohi // Share
Study: Consuming a wide variety of plant compounds is key to a longer, healthier life
By Ava Grace // Share
Cinnamon helps reduce high blood pressure
By newseditors // Share
Zionism is not an American principle
By newseditors // Share
Trump faces scrutiny over deceptive Iran bombing plan as global tensions escalate
By finnheartley // Share